Thailand Pilot
3. KKU Pilot Sites and Smart Labs

1. KKU Pilot Sites and Smart Labs

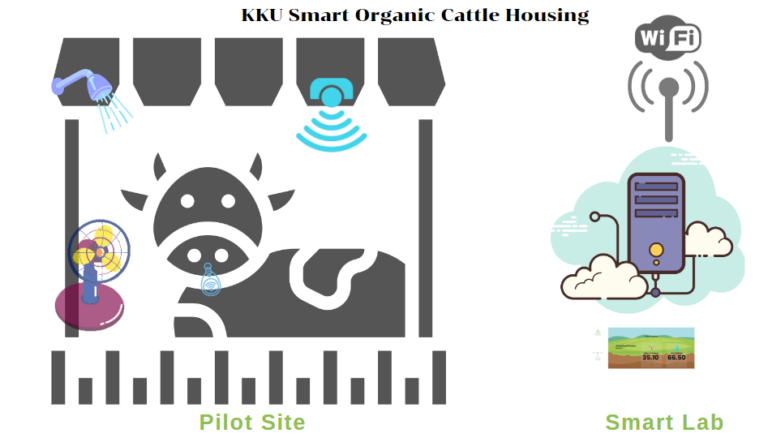
KKU Smart Organic Cattle Housing
Objective: To increase the exchange rate of meat and reduce a cow stress with the following smart tools:
- The motion sensor system for monitoring a cow’s behavior.
- The cattle housing temperature control and detection system for keep a cow cool.
- The data of cow growth rate will be collected in the data collection system with an intelligent RFID system.
The operation of KKU Smart Organic Cattle Housing
1. When the cattle come for eating, they will pass the motion sensor. The sensor will send the signal to the control box to switch on the water pump then the solenoid valve will be releasing the water to sprinklers showering a cattle’s body automatically.
2. The temperature sensor will report the real-time temperature. When the temperature in the cattle housing is higher than the setting rate, the sensor will send the signal to the control box to turn on the electric fans. And the electric fans will turn off automatically when the temperature in the cattle housing is stable.
3. The ear Tag of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) shows a cow’s data such as age, sex, height, body’s temperature, and breath rate (frequency per day), food taking (minutes/time and times/day) and weather data such as temperature and humidity, users can edit and set the ones above via the application and cloud.
4. All collected data will be stored on a cloud of the smart lab for further analysis.
KKU Smart Organic Vegetable Farm
Objective: To make organic vegetable cultivation more efficient.
- Water release control system via smartphone.
- The smart sensor system measures the level of soil moisture to provide adequate water to the plant’s needs efficiently.
- The system for detecting toxins and contaminants in water.
- The weather station for detecting climate for professional vegetable cultivation.
The operation of KKU Smart Organic Vegetable Farm
1. Soil sensors have been installed in the vegetable plot for monitoring the moisture of the vegetable plot. When the soil is dry more than the set rate, the sensor will send a signal to the control box then the irrigation system will turn on automatically. And when the soil has moisture in the rate-setting, the sensor will send the signal to the control box to turn off the irrigation system.
2. Or user will control the irrigation system via the mobile phone. Users will check the data of all sensors at the vegetable plot in real-time at the website and can turn on or turn off the irrigation system manually by phone anytime and anywhere.
3. All collected data will be stored on a cloud of the smart lab for further analysis.
2. Train the Trainer
KKU Training of the trainers is organized and hosted in Thailand. The objective is to properly upskilling and hands-on training farmers who are willing to adopt new technology to their farm in Northeastern region of Thailand. The training course provides knowledge delivered by researchers from the SUNSpACe project under the operation of Khon Kaen University. Researchers team consists of staffs from the Faculty of Business Administration and Accountancy, the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, the Faculty of Agriculture, the Faculty of Engineering and Phu Sing Agricultural Development Center due to the royal initiative. There are also researchers from SUNSpACe member countries who joined the training program
The training course is divided into 4 modules:
- Digital agriculture
- Livestock farming
- Cultivation farming
- Standardization
- Agro-business
This training module includes Internet-of-thing (IoT) in agriculture, smart monitoring and smart controlling, data processing, business modeling, occupational health topics supplemented with field visits; demonstration of agro-meteorology, soil, pH and moisture sensors, automation of irrigation equipment installed at the smart lab, integrated organic farm. Participants discuss smart farming technologies that could be adopted in Thailand. The training is conducted using both onsite and online modes due to Thailand’s regulation during Covid19 pandemic.
Smart-farm trainer profiles
Training participants: Total: 19
- Smart farmers: 12
- Academic staffs: 5
- Administrative staffs: 2
The participating farmers who are growing vegetables and livestock farming, come from 3 provinces of North-eastern region of Thailand: Khon Kaen, Maha Sarakham and Nong Bua Lamphu, their farms are located in 8 different districts: Nam Phong, Mueang Khon Kaen, Kranuan, Seechompu, Khao Suan Kwang, Kosum Phisai and Sribunruang. The subdistricts, where they are from are: Non Thon, Tha Kra Serm, Don Han, Sila, Huay Jod, Na Chan, Mueang Kao, Na Ngew, Loeng Tai, Thung Nong Mon, Bueng Niam and Ban Ped.
Training topics
- Virtual tour equipment
- Presentation skill
- Storyboard and Content creation
- Workshop: farm visit 2 round
Evaluation:
3. Farmers Training
Local Farmers Training
Training topics
- Module 1: Digital Agriculture
- Module 2.1: Livestock Farming
- Module 2.2: Cultivation Farming
- Module 3: Standardization
- Module 4: Argo-Business
Training process
Step 1: Before the training course, all selected farmers will examine as a pre-test to let trainers assess their knowledge base.
Step 2: All trainees will take a lecture class to learn the overall infrastructure of the pilot site, smart lab, system, etc.
Step 3: All trainees will learn installation processes (devices, equipment, etc.).
Step 4: Trainers will demonstrate device use (setting up, controlling, interpreting data, application and web page control, etc.).
Step 5: All trainees take an examination as a post-test to let trainers assess their new knowledge and understanding of the lessons.
Evaluation:
The results of the smart farming intention behavior assessment after the training show that most of the participants highly agree to adopt smart agriculture in their farms. From the results of the questionnaire analysis, it can be concluded that most of the participants tended to change their farming behavior from traditional to smart farming according to the training program. In addition, the KKU SUNSpACe Team observed the farming behavior of the participants to follow up on the participants who applied the knowledge gained from the training to use in their farming.
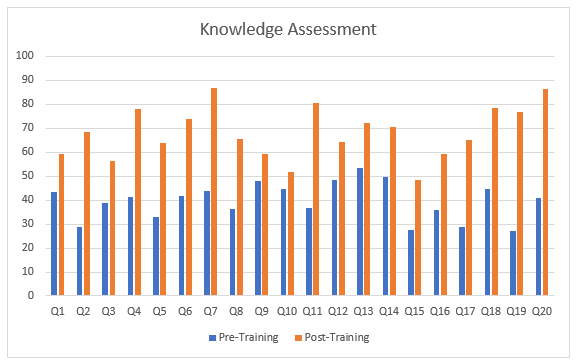
Expectation of the training is that participants should gain some knowledge, we assess knowledge of participants using questionnaire consisting of 20 questions relevant to smart monitoring covering general definitions of smart farming devices, their functions of them, some relationships among parameters and crops.
- Average Pre-test score: 7.25 scores out of 18 total scores
- Average Post-test score: 13 score out of 18 total scores
4. On Farm Practice
Number of farm installaed: Total 250 farms
- Farm visit
- the memorandum ceremony between the Faculty of Bussiness Administration and Accountancy (KKBS)
- KKU SUNSpACe Workshop for Farmer
- KKU SUNSpACe Webinar 2021: Sustainable & Smart Agriculture
- KKU SUNSpACe Ornamental Plants Varieties with Smart Technology














































































































